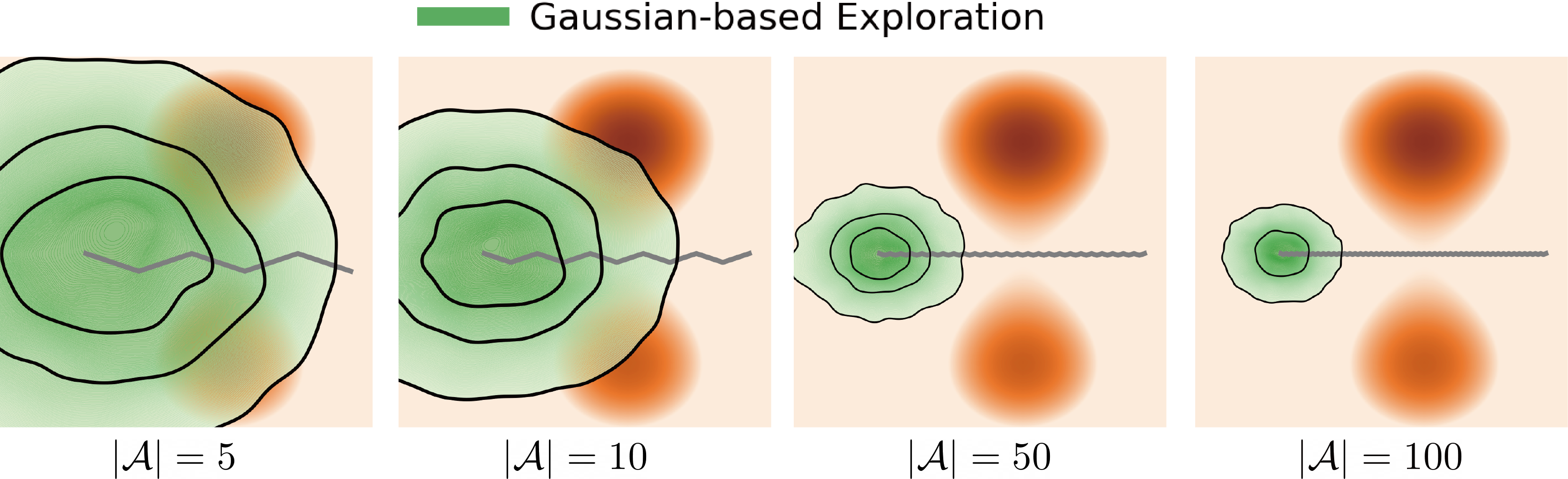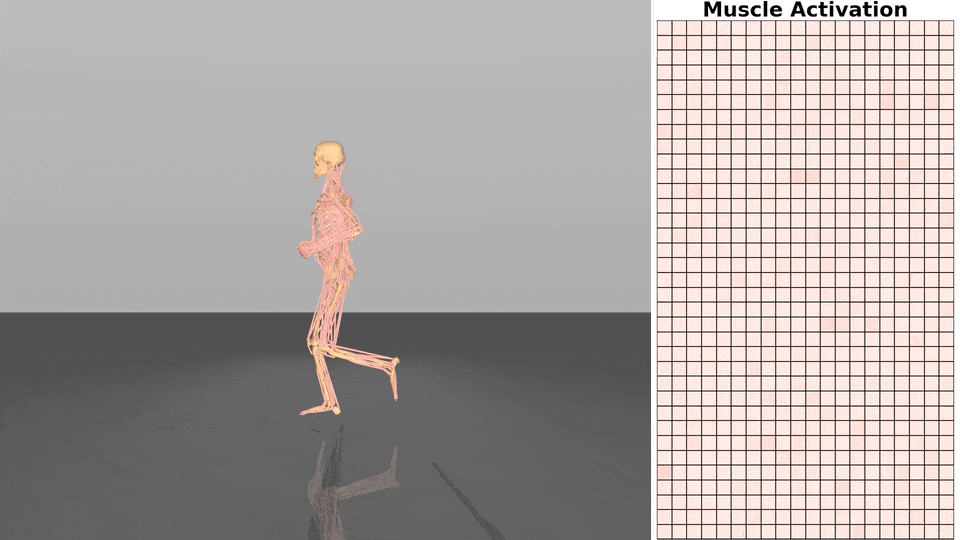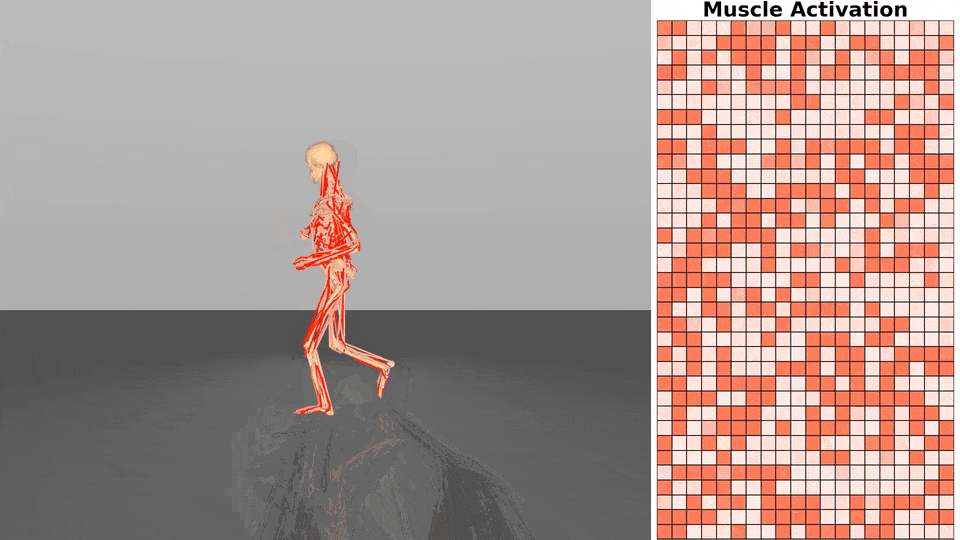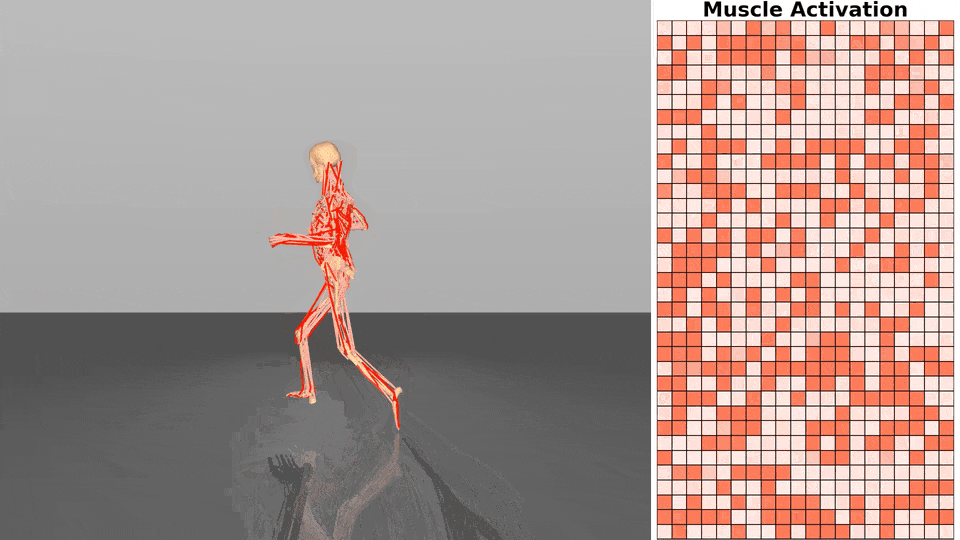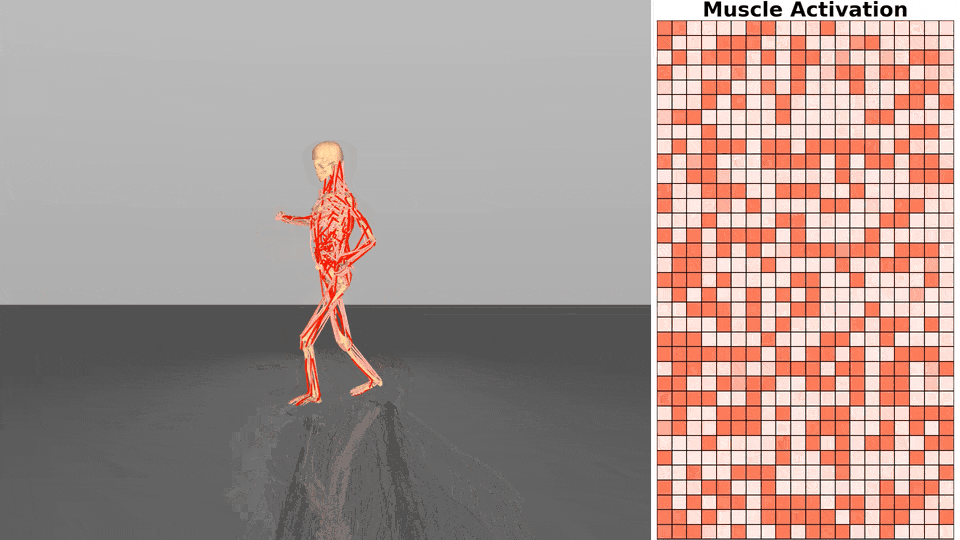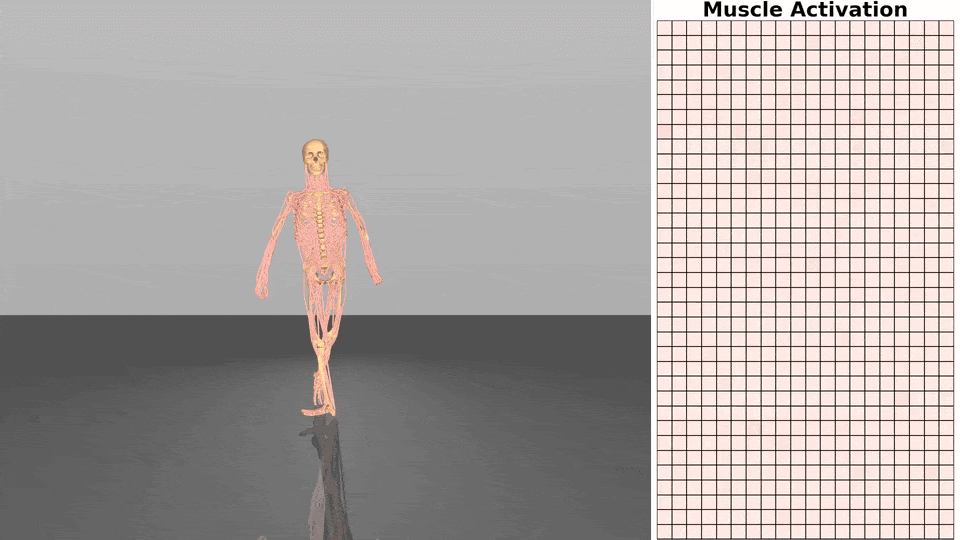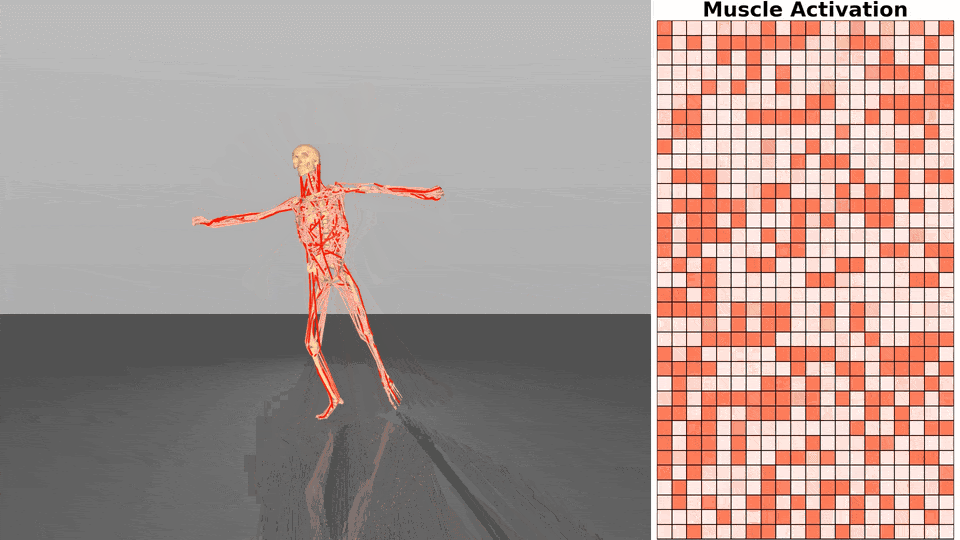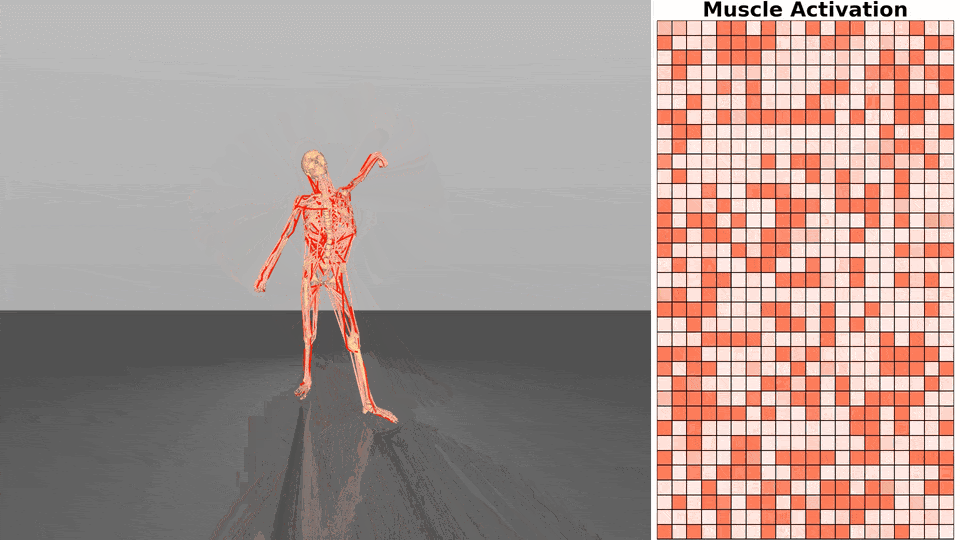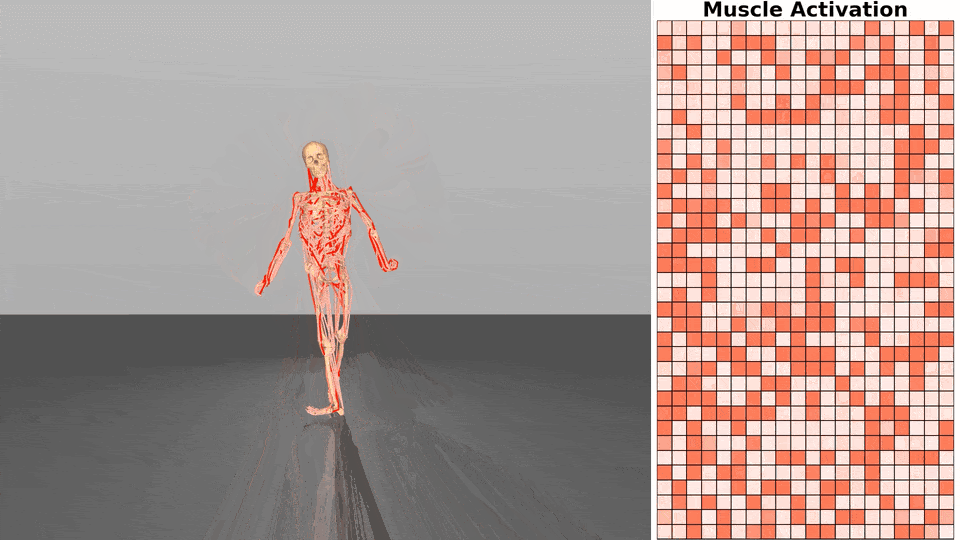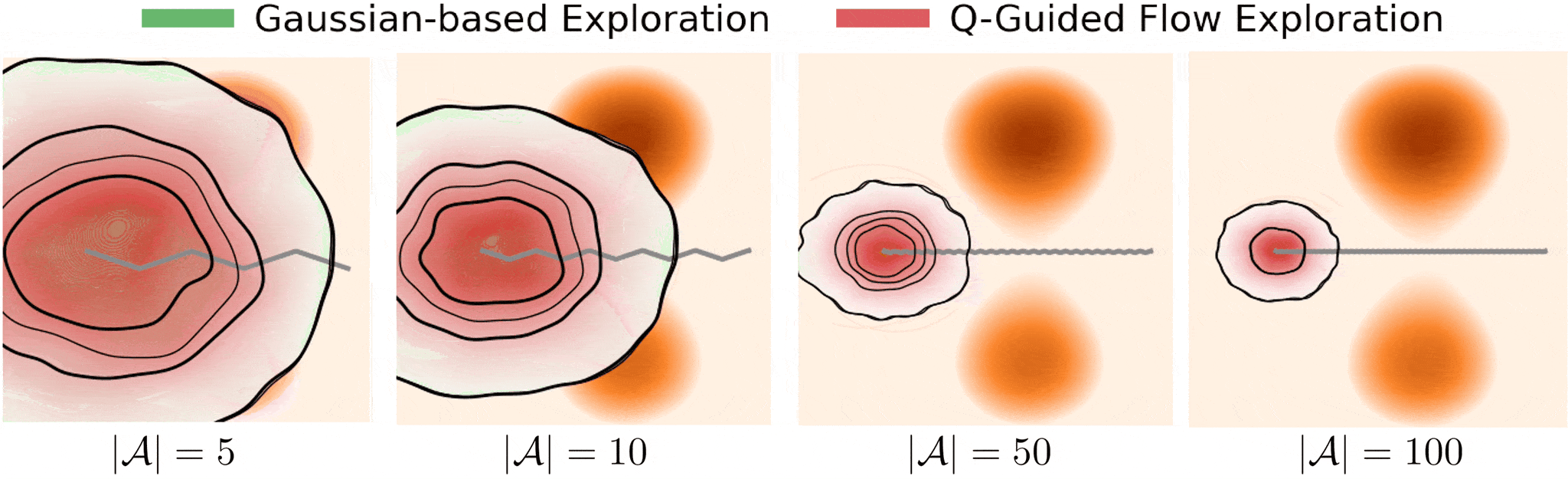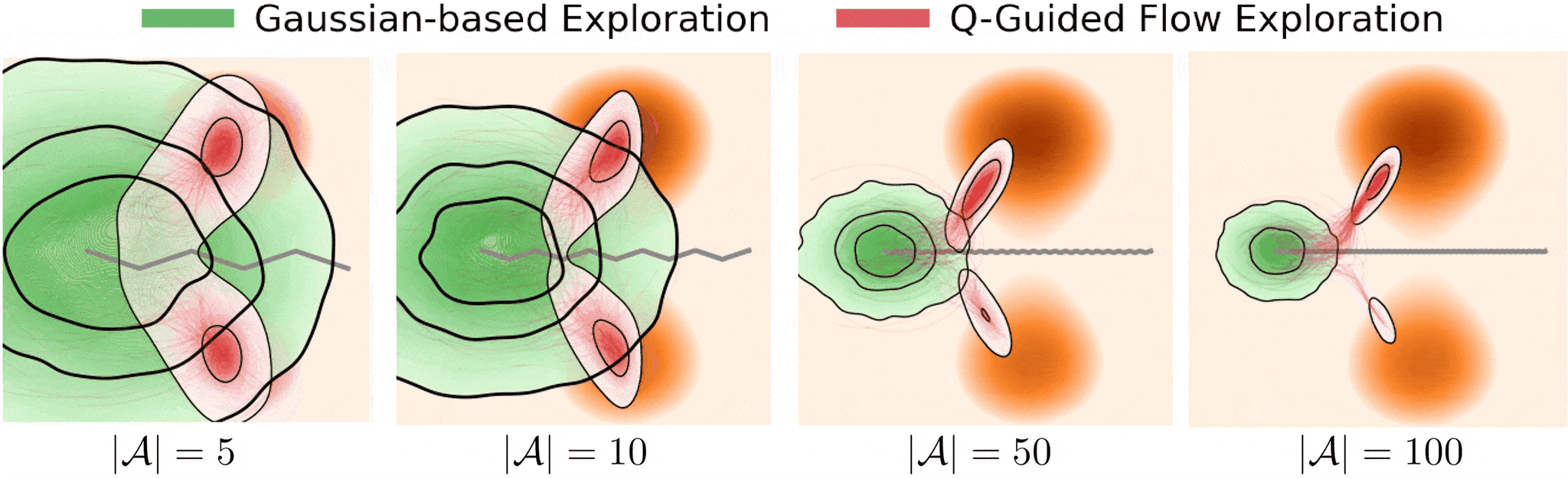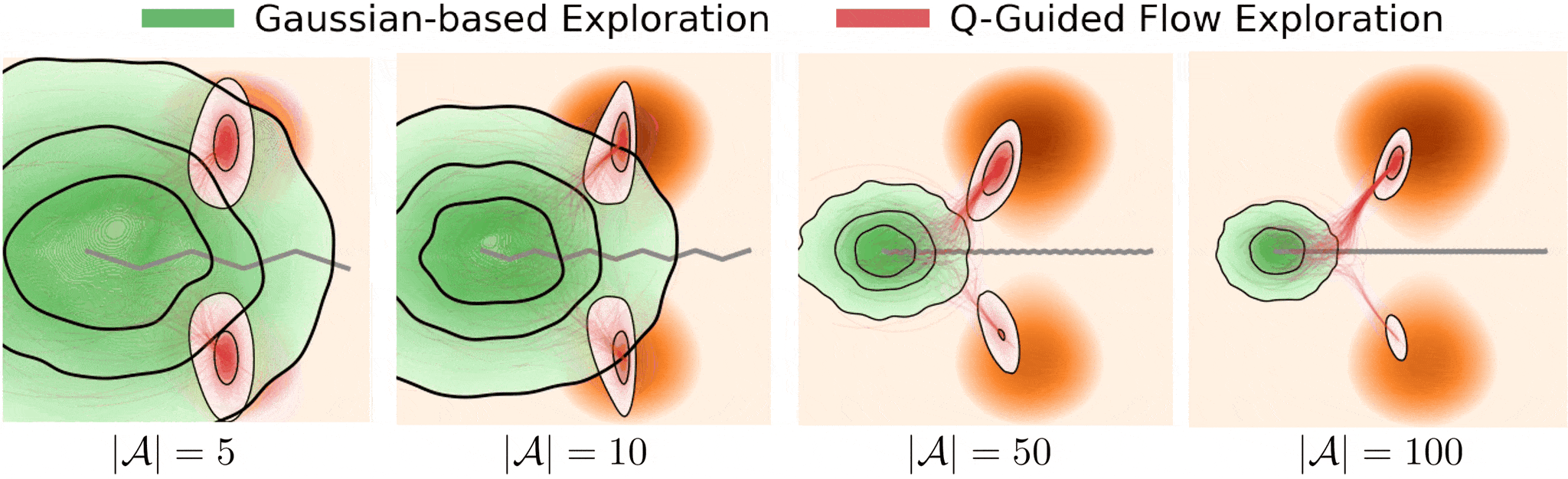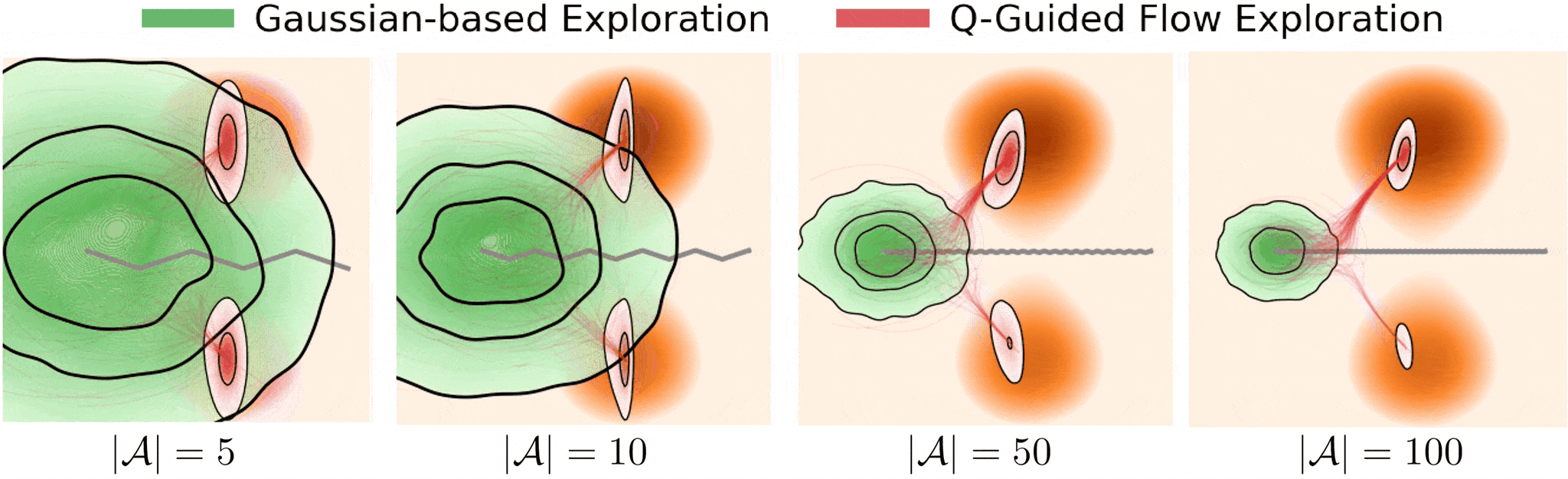
Figure 1. Exloration behavior across increasing dimensionality.
Gaussian-based exploration: undirected exploration where exploratory collapses as system dymensionality increases.
Q-guided flow exploration (ours): directed exploration towards high-value modes in high dimensions by following value-guided flow
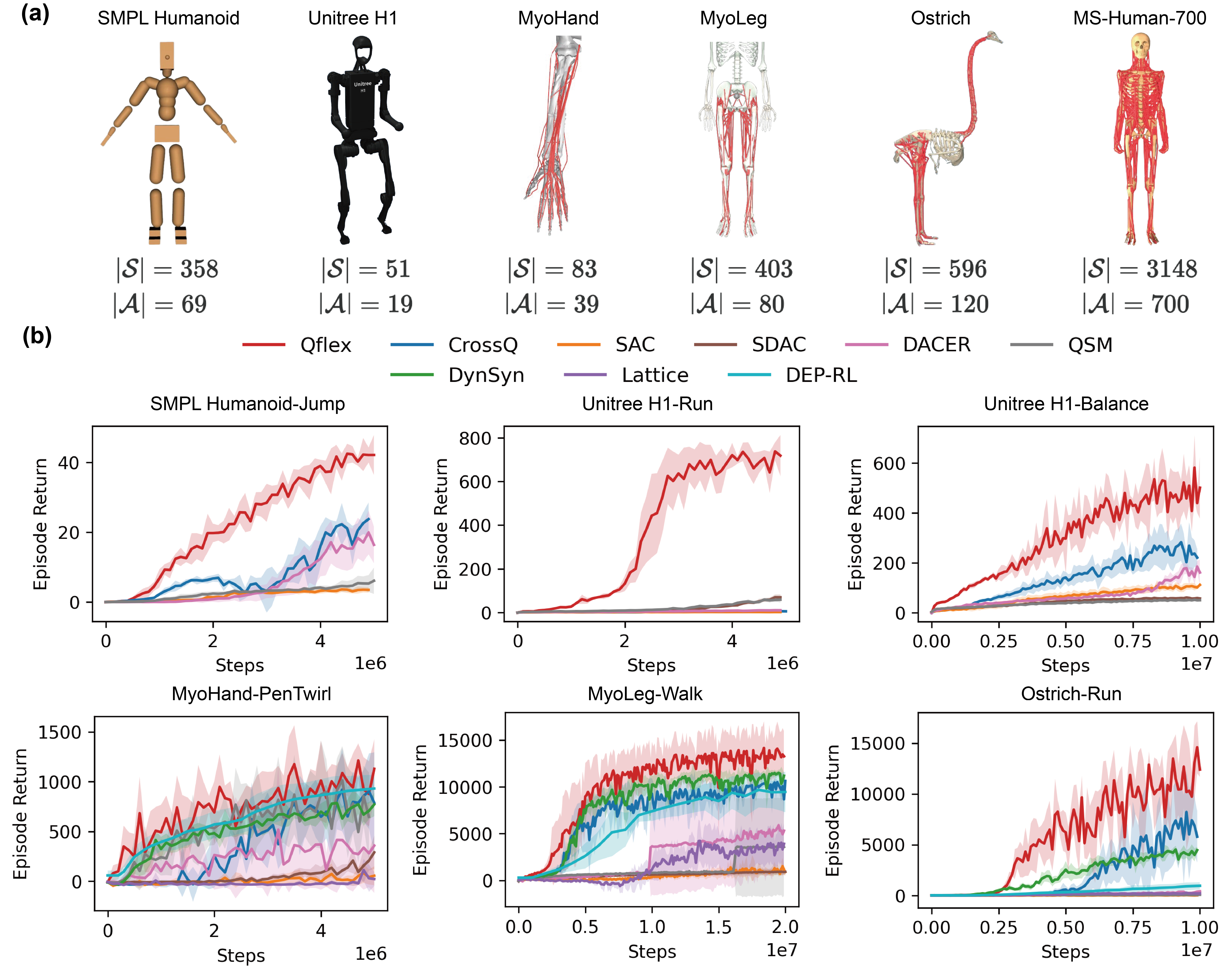
In this paper, we aim to develop a scalable and efficient online reinforcement learning (RL) method for continuous control of high-dimensional dynamical systems. Such systems often present challenges that significantly hinder efficient learning:
We expect the control method to have the following properties:
• High-dimensionality: The size of the state-action space grows rapidly with dimension, leading to pronounced “curse-of-dimensionality” effects
• Over-actuation: multiple action sequences can yield indistinguishable kinematics but different internal forces and costs given much more actuators than degrees-of-freedom
These challenges make effective exploration crucial for both learning efficiency and control performance.